Smart Home Security: Integrating Technology for Maximum Protection

Welcome to Deep Dive Picks, where we bring you the most in‑depth news, reviews and expert analysis to help you make informed decisions. In today’s rapidly evolving connected‑home world, achieving robust Home Security requires far more than simply installing a camera or alarm system. With the rise of smart devices, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, artificial intelligence, and interconnected ecosystems, a smart‑integrated strategy is the most effective path to maximum protection. In this detailed article we will explore the foundation of smart home security, delve into the latest technologies and integration best‑practices, examine common risks and mitigation strategies, and provide you with actionable steps to build a holistic protection strategy for your home.
The Changing Landscape of Home Security
The concept of home security has evolved substantially in recent years. While traditional systems relied on hard‑wired alarms, door and window sensors, and a central monitoring station, modern setups are becoming dynamic, adaptive and integrated into broader smart‑home ecosystems. Market data show that the global smart home security market was estimated at USD 33.94 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 82.07 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of approximately 15.2 %.
Moreover, surveys indicate a shift in homeowner behaviour: more users are embracing smart devices for peace of mind, remote monitoring and lifestyle integration rather than solely for intruder deterrence. For example, one recent U.S. study found that 48 % of homeowners cited peace of mind as the primary motivation for adopting security systems, while 29 % cited burglary or theft protection.
This change demands that we rethink home security not as a standalone alarm box, but as an ecosystem of sensors, connectivity, intelligence and automation—working together to detect, deter, respond and recover.

Key Concepts for Smart Home Security Integration
To successfully integrate a smart home security solution, we must understand several core concepts: connectivity and interoperability, layered protection, intelligence and automation, and user‑centric design.
Connectivity & Interoperability
At the heart of a modern home security ecosystem lies connectivity. Devices such as cameras, door sensors, smart locks, motion detectors and alarms must communicate reliably—both with each other and with a central hub or gateway. Wireless technologies (Wi‑Fi, Zigbee, Z‑Wave, Thread) and wired back‑bones play a role. Interoperability is equally important: devices from different manufacturers must be able to interact, share alerts and integrate into the same automation rules. Without interoperability, you end up with fragmented systems and blind spots in your home security strategy.
Layered Protection Architecture
An effective home security framework uses a layered protection architecture. That means implementing multiple overlapping layers—physical deterrence (locks, lighting), sensing (cameras, motion detectors), access control (smart locks, digital keys), monitoring and alerting (notifications, remote control), and recovery (cloud storage, logs, incident response).
For example, the combination of visible outdoor cameras, motion‑activated lighting, and a smart lock with analytics creates more deterrence, detection and response capacity than any one layer alone. Surveys show that many users combine outdoor cameras with smoke or carbon-monoxide detectors for comprehensive coverage.
Intelligence & Automation
Modern home security systems increasingly rely on intelligence: AI‑driven analytics, anomaly detection, behavioural profiling and automation routines. For example, smart cameras might detect not just general motion, but distinguish between humans, vehicles, pets or packages—reducing false alarms and improving relevance.
Automation, in turn, allows triggers (e.g., smart door opens) to initiate actions (turn on hall light, record video, send push notification, lock doors) without manual intervention. This creates responsiveness and ensures your home security system works proactively.
User‑Centric Design & Experience
Focusing on user experience matters. Even the most advanced home security system fails if users disable notifications, ignore warnings, or struggle to control it. Concerns around privacy, device usability and network trustworthiness influence adoption and ongoing usage.
Thus, designing your system around clear interfaces, reliable alerts, low‑maintenance devices, and transparent privacy practices is essential for sustainable protection.
Core Components of Smart Home Security Systems
Now let’s break down the main hardware and software components that form a modern smart home security ecosystem. We will explore each component’s role, key considerations and integration best‑practices.
Smart Cameras & Video Doorbells
Smart cameras (indoor/outdoor) and video doorbells are among the most visible and adopted aspects of home security. When choosing cameras, important factors include resolution (1080p, 2K, 4K), field of view, night vision, weather proofing, on‑board or cloud storage, two‑way audio, mobile push notifications and integration with other devices (smart locks, lighting).
Integration best‑practice: Connect your camera feeds with your automation hub so that, for example, when motion is detected on the front porch after 10 pm, it triggers porch lighting and notifies your smartphone. Also, ensure the video doorbell is integrated with your smart lock or entry system to allow remote verification and voice communication with visitors.
Be mindful of privacy and data security: Ensure firmware updates, encrypted storage and access control are in place.
Smart Locks & Access Control
Smart locks offer the next layer of protection by managing who enters your home and when. In 2025, smart locking technology continues to evolve with new interoperability standards.
When integrating smart locks into your broader home security system, consider remote locking/unlocking, notifications when doors are left open, integration with alarms for auto-locking, multiple user codes or digital keys with audit logs.
Access control systems should tie back into your monitoring and alerting system: a failed attempt to unlock during a set time should trigger a high-priority alert rather than just a log entry.
Motion & Contact Sensors
Motion sensors and contact sensors form the sensing backbone of your home security architecture. These devices detect intrusion, unauthorized openings, or unusual movement and feed into alarm or automation triggers.
Best practice: Place motion sensors in vulnerable areas and configure zones to avoid false alarms. Contact sensors should be installed on all entry points and linked with event logs/alerts. Integrate with automation so that if a contact sensor is triggered while the system is armed, cameras begin recording, lights turn on, and mobile alerts are sent.
Alarm Systems & Sirens
Modern alarm systems are no longer just a loud siren and flashing light. In a connected smart home security environment, alarms integrate into the device network, mobile apps and cloud services.
Ensure your alarm system supports professional monitoring, mobile self‑monitoring, power‑outage backup batteries, and tamper detection. Integrate the siren with other components like lighting and cameras to enhance deterrence and response.
Environmental & Safety Sensors
A comprehensive home security plan extends beyond burglary to include safety threats such as fire, carbon monoxide, flooding and gas leaks. Smart smoke detectors, carbon monoxide detectors and flood sensors are increasingly being adopted.
Integration best‑practice: Tie these sensors into your automation system so that a flood sensor triggers water shut‑off, smart lighting guidance to the exit, or mobile alerts to key contacts.
Smart Lighting & Deterrence Systems
Smart exterior lights, floodlights with cameras, motion‑activated lighting, and timed lighting routines create the impression of occupancy and vigilance.
Integration with cameras and sensors allows lights to respond to triggers like motion detection. Deterrence systems such as audible announcements from outdoor speakers and signage can reinforce security presence.
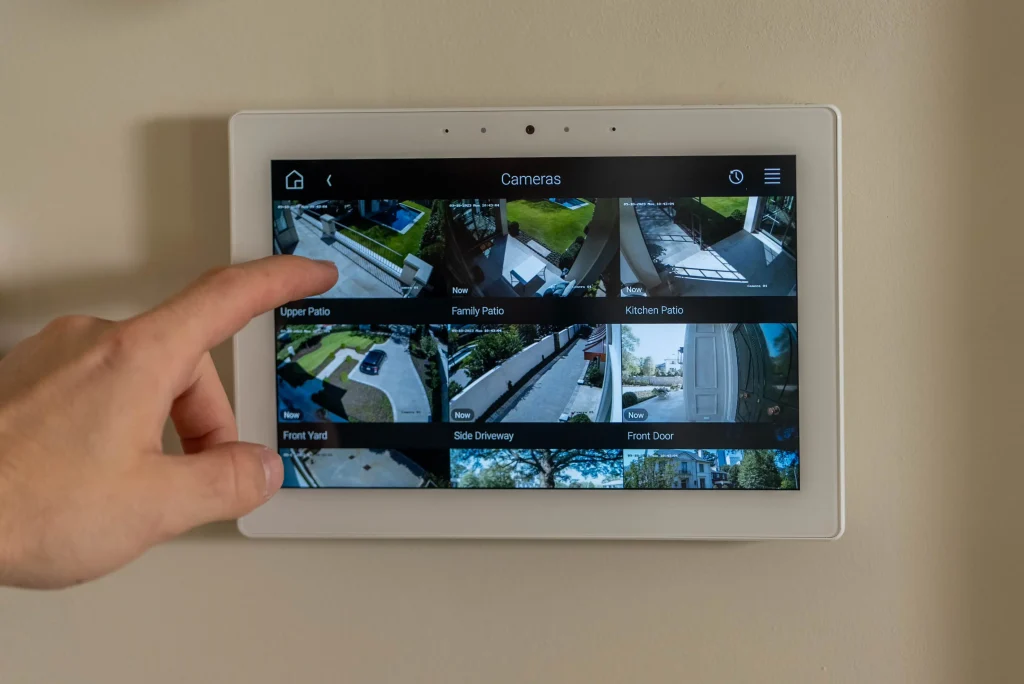
Mobile Apps, Alerts & Remote Monitoring
A truly smart home security system places control and visibility in your palm. Mobile apps enable remote arming/disarming, live feeds, alerts, automation configuration, and system status checks.
Effective remote monitoring requires multi-user access, role-based permissions, two-factor authentication, encrypted communications, and access logging.
Cloud Services & Edge Processing
Cloud storage and monitoring provide flexibility and scalability, while edge processing on devices reduces latency and enhances privacy.
Edge processing allows cameras and sensors to analyze footage locally and only send relevant events, reducing bandwidth usage and potential data exposure.
Integrating Your Security System into a Unified Ecosystem
Building independent smart devices is only one step. Integration ensures your smart home security system is cohesive, responsive and manageable.
Establish a Smart Home Hub or Platform
Platforms like Apple HomeKit, Google Home, or Amazon Alexa allow unified control, automation routines, and alerts across multiple devices. Integration enables complex scenarios like locking all doors, arming sensors, and activating lighting when the system is set to “away.”
Define Automation Rules & Scenarios
Automation rules link components to respond intelligently. Examples include turning on lights and cameras when motion is detected at night, triggering notifications for abnormal activity, and automating door locks in emergency situations. Layered automation enhances protection and reduces false alarms.
Monitor & Maintain Continuously
Continuous monitoring and maintenance are vital. This includes firmware updates, battery checks, connectivity health, and reviewing event logs. Neglected devices can undermine the system’s effectiveness.
Privacy & Cybersecurity Considerations
Smart home security systems expose new attack surfaces. Segment networks, enforce strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, update firmware, and minimize data retention to protect against cyber threats.
Emerging Trends & Future-Proofing Your Home Security
Understanding future trends ensures long-term effectiveness.
Artificial Intelligence & Behavioural Analytics
AI moves from simple motion detection to behavioral analytics and anomaly detection, reducing false positives and enhancing responsiveness.
Standardization & Interoperability
Universal standards like Matter and Thread enable devices from different manufacturers to work together seamlessly, simplifying integration and future upgrades.
Smart Homes as Lifestyle Ecosystems
Smart home security is increasingly integrated into broader lifestyle ecosystems, monitoring well-being, energy usage, and emergency situations alongside security.
Privacy Labels & Consumer Trust
Certified devices and privacy standards help consumers evaluate the security of IoT devices, building trust and future-proofing the system.
Hybrid Monitoring and DIY Kits
Homeowners increasingly adopt hybrid or self-monitored solutions, blending professional monitoring with self-managed devices for flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Designing Your Smart Home Security Strategy Step-by-Step
Assess your home’s risk profile and perimeter. Define protection goals and budget. Select a central platform/hub with interoperability. Choose core devices first: cameras, locks, sensors. Design automation and integration rules. Secure your network architecture. Install and configure devices, test functionality. Establish monitoring and response protocols. Perform regular maintenance and review logs. Upgrade and scale over time.
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
Fragmented Systems and Lack of Integration
Mitigate by selecting a compatible platform and testing automation scenarios.
False Alarms and Alert Fatigue
Mitigate by optimizing sensor placement and using analytic-enabled devices.
Network Vulnerabilities and Device Exploits
Mitigate by segmenting devices, changing default credentials, and maintaining updates.
Over-Reliance on a Single Component
Adopt a layered protection approach combining cameras, locks, sensors, lighting, monitoring, and automation.
Poor User Adoption or Maintenance
Choose user-friendly interfaces, schedule regular checks, and train household members on the system.
Measuring Effectiveness and ROI of Your Home Security System
Evaluate through reduction in incidents, deterrence and insurance benefits, long-term system value, and user satisfaction.
Case Study: Integrating Smart Home Security in a Modern Home
A family installs a smart-home hub, outdoor cameras, video doorbell, motion and contact sensors, smart locks, and environmental sensors. Automation and integration create a layered system that alerts, records, and deters intrusions. Network segmentation and regular maintenance maintain security, while the family benefits from peace of mind and insurance savings.
Final Thoughts: Making Smart Home Security Work For You
Smart home security requires holistic integration, intelligence, and user-centric design. Proper planning, maintenance, and cybersecurity measures ensure maximum protection, resilience, and peace of mind. Future-proof your system with interoperable devices, AI analytics, and hybrid monitoring options.
Conclusion
Integrating technology into your home security strategy is essential for maximum protection. Treating your system as an ecosystem—rather than a standalone device—enhances deterrence, detection, automation, and control. With thoughtful selection, integration, automation, security, and maintenance, your home becomes a resilient, responsive environment that delivers safety and peace of mind. You can find more details on our homepage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between smart and traditional home security systems?
Smart home security systems incorporate connected devices that allow remote monitoring, automation, and integration with a smart-home ecosystem. Traditional systems are often hard-wired with limited access and minimal automation.
How do I ensure my smart home security system is protected from hacking?
Segment IoT/security devices on a separate network, use strong unique passwords and two-factor authentication, enable automatic updates, and review access logs regularly.
Can I integrate devices from different manufacturers into one security system?
Yes, by using a hub or platform that supports interoperability standards, devices from different vendors can communicate, trigger automation rules, and present a unified interface.
What automation rules should I set up for maximum protection?
Automation rules can include arming the system when away, triggering cameras and lighting upon motion, linking door locks with alarms, and integrating environmental sensors for fire or flood alerts.
How often should I review or update my home security system?
Check battery levels, connectivity, and logs monthly. Install updates as they become available. Review system architecture and automation rules bi-annually or annually to ensure ongoing effectiveness.