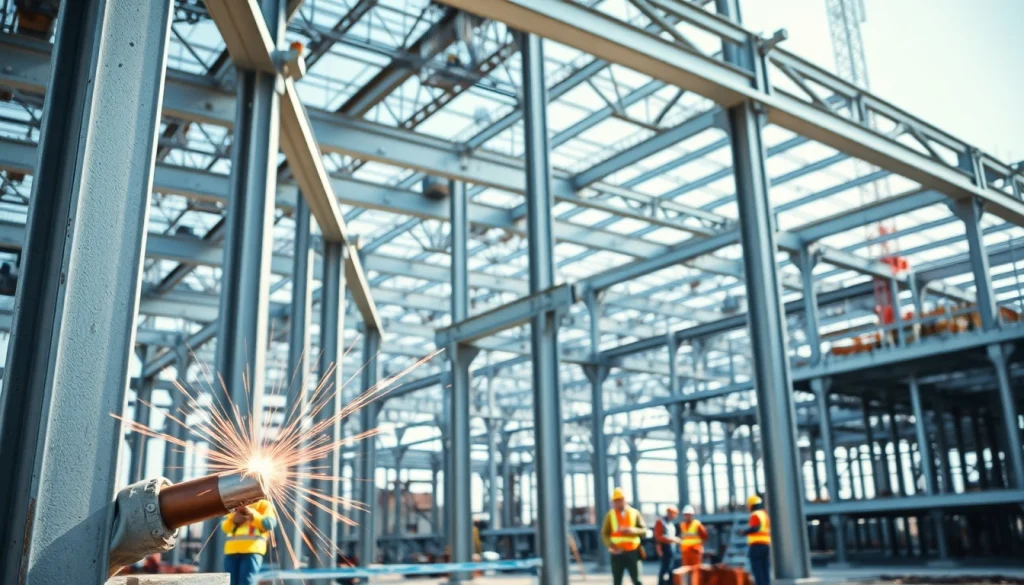
Understanding Structural Steel Construction
Structural steel construction plays a vital role in modern architecture and engineering, serving as the backbone for various types of buildings and infrastructures. This durable and versatile material is essential for achieving structural integrity and flexibility in design. Throughout this article, we will delve deep into structural steel construction, its components, benefits, challenges, best practices, and key performance metrics.
Definition and Importance of Structural Steel
Structural steel is a category of steel used for making construction materials for a variety of purposes. It is produced in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different engineering designs and is characterized by its high strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and reliability. The importance of structural steel extends beyond mere utility; it facilitates advancements in engineering design and allows for innovative architectural solutions.
Key Components in Structural Steel Fabrication
The fabrication of structural steel involves a series of processes and components that are fundamental to the overall construction framework. Key components include:
- Structural steel beams – Used to support loads across spans.
- Columns – Vertical structural elements that bear the weight of beams and slabs.
- Steel plates – Flat pieces of steel used for various reinforcing and structural purposes.
- Joists – Long, horizontal structural members that support floor systems.
- Trusses – Frameworks of triangular shapes that distribute loads effectively.
Understanding the intricacies of these components is essential for anyone involved in structural steel construction, as their interaction forms the skeletal frame of any significant structure.
Common Applications of Structural Steel in Construction
Structural steel is employed in a wide range of applications within the construction sector, including:
- Commercial buildings – Often the preferred material for skyscrapers and large complexes due to its strength.
- Industrial structures – Used extensively in factories, warehouses, and power plants.
- Bridges – Essential for creating strong, durable spans that can withstand significant environmental forces.
- Residential buildings – Increasingly common for new home designs and renovations.
- Infrastructure projects – Such as airports, malls, and sports complexes where extensive load-bearing capacity is critical.
These applications illustrate the versatility of structural steel in meeting various engineering requirements and aesthetic designs.
Benefits of Using Structural Steel Construction
Cost Efficiency and Sustainability
One of the most significant advantages of structural steel construction is its cost efficiency. The material allows for quicker construction timelines, which can lead to reduced labor costs and timely project delivery. Additionally, structural steel is inherently recyclable, supporting sustainable construction practices. The lifecycle of structural steel—from fabrication to recycling—offers environmentally friendly advantages, minimizing waste and conserving resources.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Structural steel enables architects and engineers to push the boundaries of design. The material can be molded into various shapes and sizes, allowing for intricate, modern designs without compromising stability. This adaptability not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also provides unique solutions to architectural challenges. Structural steel’s sleek appearance complements contemporary designs, helping to create standout structures in any urban landscape.
Strength and Durability Advantages
Structural steel is renowned for its strength and durability. It can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including high winds, heavy snow loads, and seismic activity. This resilience is essential for safety and longevity in structures. Unlike other materials, structural steel does not warp, crack, or settle over time, providing a durable and long-lasting foundation for various constructions.
Challenges Faced in Structural Steel Construction
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
The construction industry is heavily regulated, and structural steel projects must comply with various codes and standards. Meeting these safety regulations can be challenging, especially when integrating new materials or construction techniques. Builders and fabricators must remain updated on regulations to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal repercussions or project delays.
Logistical Issues in Material Sourcing
While structural steel is widely available, logistical challenges can arise in sourcing materials. Factors such as supply chain disruptions, fluctuating prices, and delays can impact project timelines. To mitigate these challenges, firms must establish reliable supply chains and strategic partnerships with steel manufacturers to secure quality materials promptly.
Skilled Labor Shortages in the Industry
The construction industry faces a significant shortage of skilled labor, impacting structural steel projects. The need for experienced welders, fabricators, and engineers is on the rise. Companies must invest in training and development programs to cultivate a skilled workforce capable of navigating the technical demands of structural steel construction.
Best Practices for Successful Structural Steel Projects
Effective Project Management Techniques
Effective project management is crucial in ensuring the success of structural steel projects. Employing methodologies such as lean construction practices can help streamline processes and enhance efficiency. Additionally, utilizing project management software to track timelines, budgets, and resources can lead to improved coordination and communication among project stakeholders.
Incorporating Advanced Technology in Construction
The integration of advanced technologies, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and robotics, can enhance structural steel construction practices. BIM allows for detailed planning and visualization before construction begins, minimizing errors and reworks. Robotics can streamline repetitive tasks, improving productivity and safety on worksites.
Continuous Training for Construction Teams
To stay competitive, continuous training for construction teams is essential. Regular training helps workers adapt to new technologies, techniques, and safety practices in structural steel construction. Investing in ongoing education fosters a culture of learning and ensures that teams can meet evolving industry demands.
Metrics for Measuring Success in Structural Steel Construction
Key Performance Indicators You Should Track
To measure the success of structural steel projects, it is essential to establish key performance indicators (KPIs). Common KPIs include project completion time, budget adherence, quality control measures, and safety incident rates. Monitoring these metrics allows construction firms to identify areas for improvement and optimize project performance.
Evaluating Project Timeliness and Budget Adherence
Timeliness and budget adherence are critical metrics for evaluating the overall success of construction projects. Regularly assessing project timelines against estimated completion dates helps identify potential delays early. Similarly, tracking expenditures against the budget can ensure that costs remain manageable and within the agreed-upon limits.
Client Satisfaction and Post-Project Review Processes
Ultimately, client satisfaction is a vital indicator of project success. Conducting post-project reviews can provide valuable insights into the overall experience, allowing teams to gather feedback, assess strengths and weaknesses, and implement improvements for future projects. Engaging clients throughout the process can also enhance relationships and promote repeat business.